

 |
 |
| Carbon | |
| Electron Configuration | 2,4 |
| Electron Configuration | 1s2 2s2 2p2 |
| Ground state | 3P0 |
| Atomic Volume | 4.58 g/cm3 |
| Electronegativity | 2.55 |
| Magnetic ordering | Diamagnetic |
| Mass magnetic susceptibility | -6.2 x 10-9 |
| Molar magnetic susceptibility | -7.45 x 10-11 |
 Thermal Properties Thermal Properties |
|
| Enthalpy of Atomization | No data. |
| Enthalpy of Fusion | 105.0 kJ mol-1 |
| Enthalpy of Vaporisation | 710.9 kJ mol-1 |
| Heat Capacity | (graphite) 8.517 J mol-1 K-1 |
| Thermal Conductivity | (graphite) 119-165 W m-1 K-1 |
| Thermal Expansion | No data. |
 Hardness Hardness |
|
| Mohs hardness | 1-2 graphite, 10 diamond |
 Electrical Properties Electrical Properties |
|
| Electrical resistivity | No data. |
| Electrical conductivity | No data. |
 Chemical Properties Chemical Properties |
|
| Ionization Potential | |
| 11.26 | |
| 24.383 | |
| 47.887 | |
| Incompatibilities | Very strong oxidizers such as fluorine, chlorine trifluoride (ClF3)and potassium peroxide (K2O2). |
 Flammability Flammability |
|
 Optical Properties Optical Properties |
|
| Refractive Index (solid) | 2.417 (diamond) |
 Energy Levels Energy Levels |
|
| 0.277 KeV | |
 Atomic Radii Atomic Radii |
|
| 70 pm | |
| 67 pm | |
| 77 pm | |
| 170 pm | |
| 60 pm | |
| No data. | |
 Ionic Radii (Å) Ionic Radii (Å) |
||||
| Charge | Coordination | Crystal | Ionic | Key |
| 4 | III | 0.06 | -0.08 | |
| IV | 0.29 | 0.15 | P | |
| VI | 0.3 | 0.16 | A | |
| R, From r3 vs V plots. |
| C, Calculated from bond length - bond strength equations. |
| E, Estimated. |
| *, Most Reliable. |
| M, From Metallic Oxides. |
| A, Ahrens (1952) Ionic radius. |
| P, Pauling's (1960) Crystal Radius. |
 Oxidation States Oxidation States |
|
| C-4, C+2, C+4 | |
 Ionisation Energies (kJ mol-1) Ionisation Energies (kJ mol-1)  |
|
| 1086.2 | |
| 2352 | |
| 4620 | |
| 6222 | |
| 37827 | |
| 47270 | |
 Covalent Bonds (kJ mol-1) Covalent Bonds (kJ mol-1) |
|
| 411 | |
| 348 | |
| 614 | |
 C C
|
839 |
| 615 | |
 N N
|
891 |
| 745 | |
 O O
|
1074 |
 Vapour Pressure Vapour Pressure |
||||||
| P (Pa) | 1 | 10 | 100 | 1K | 10K | 100K |
| T (K) | 2839 | 3048 | 3289 | 3572 | 3908 | |
 Crystal Structure Crystal Structure |
|
| Hexagonal close packed | |
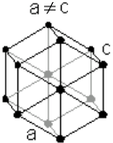 |
a = 246.4 pm |
| b = 246.4 pm | |
| c = 671.1 pm | |
| α = 90° | |
| β = 90° | |
| γ = 120° | |