| Neutrons are uncharged particles found within atomic nuclei. Neutrons were discovered by James Chadwick in 1932.
|
| The number of neutrons determines the isotope of an element. (For example, the carbon-12 isotope has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, while the carbon-14 isotope has 6 protons and 8 neutrons.) Isotopes are atoms of the same element
that have the same atomic number but different masses due to a different number of neutrons.
|
| A neutron is classified as a baryon, and consists of two down quarks and one up quark.
|
| The proper symbol to use when representing a neutron; |
|
|




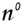
 See Also
See Also